Understanding Melanin Pigment: The Science Behind Your Skin's Color
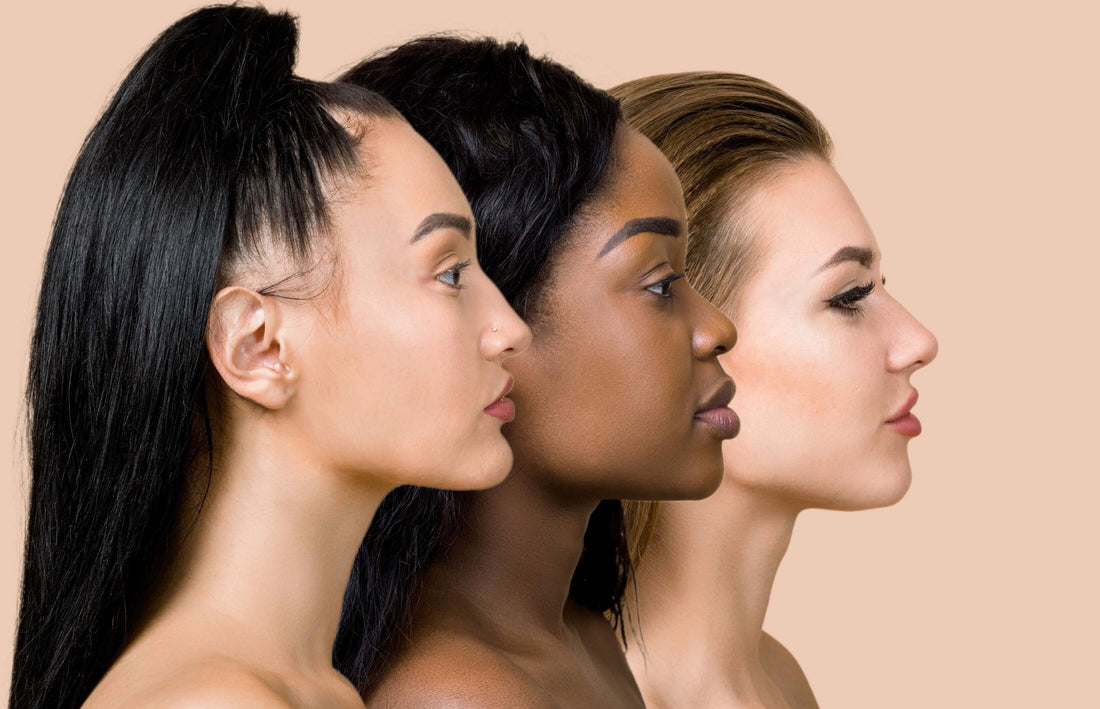
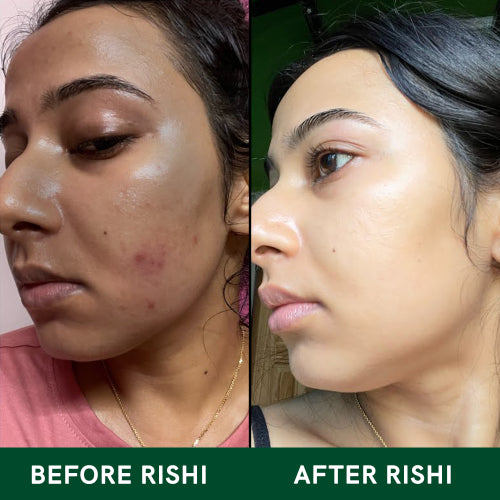
Rishi NaturalMelanin is an incredible pigment that not only determines melanin and skin color but also serves as a natural shield against environmental damage. This essential melanin pigment in skin is produced by melanocyte skin cells, primarily located in the basal layer of the epidermis. The presence of melanin for skin color varies among individuals, influencing the wide spectrum of human complexions.
Understanding skin melanin is vital, as its production can be influenced by genetics, sun exposure, and lifestyle choices. While some seek ways to increase melanin for enhanced protection, others focus on melanin reducing methods to achieve a lighter tone. Factors such as aging and certain medical conditions can lead to skin losing melanin, affecting overall complexion and protection against UV rays.
Many individuals explore treatments for reducing melanin in skin or decrease melanin in face to achieve an even skin tone. At the same time, maintaining melanin body balance is crucial for skin health. Whether focusing on melanin face treatments or understanding melanin use in protecting the skin, this pigment plays a fundamental role in our overall appearance and well-being.
In this blog, we dive into the fascinating science behind melanin and skin, its types, functions, and the various factors that influence its production, ensuring you have all the information needed to better understand and care for your melanin pigment in skin.
Table Of Content
2.1 Eumelanin
2.2 Pheomelanin
2.3 Neuromelanin
3.1 Protection Against UV Radiation
3.2 Antioxidant Properties
3.3 Thermoregulation
3.4 Neuroprotection
4. Factors Influencing Melanin Production
6. Boosting or Reducing Melanin Naturally
8. Conclusion
1. What is Melanin?
Melanin is a natural pigment produced through a complex biochemical process known as melanogenesis. The primary building block of melanin is the amino acid tyrosine, which is converted into melanin by the action of the enzyme tyrosinase. This pigment is responsible for a wide spectrum of colors in human features, from pale to dark tones.
2. Types of Melanin
There are three primary types of melanin:
2.1 Eumelanin
- Found predominantly in hair and skin.
- Exists in two subtypes: black eumelanin and brown eumelanin.
- Provides darker pigmentation and offers greater protection against UV radiation.
2.2 Pheomelanin
- Imparts a reddish-yellow hue.
- Predominantly found in red hair and lighter skin tones.
- Offers less UV protection compared to eumelanin.
2.3 Neuromelanin
- Found in specific regions of the brain.
- Plays a role in the functioning of the central nervous system.
X - MAC - Melanoma Action Coalition licensed under CC BY 2.0
3. Functions of Melanin
Melanin’s importance extends far beyond aesthetics. Here are its key roles:
3.1 Protection Against UV Radiation
Melanin absorbs and dissipates harmful ultraviolet rays, reducing the risk of DNA damage and skin cancer.
3.2 Antioxidant Properties
Acts as a free radical scavenger, protecting cells from oxidative stress.
3.3 Thermoregulation
Helps maintain body temperature by absorbing or reflecting sunlight.
3.4 Neuroprotection
Neuromelanin may help protect neurons from toxins in the brain.
4. Factors Influencing Melanin Production
Several factors affect melanin levels in the body:
- Genetics: Your genetic makeup determines the baseline level of melanin.
- Sun Exposure: UV radiation stimulates melanocytes to produce more melanin, leading to tanning.
- Hormones: Hormonal changes, such as during pregnancy or puberty, can influence melanin production.
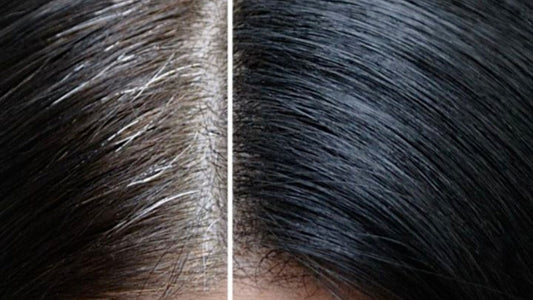
- Age: Melanin production may decrease with age, leading to graying hair and uneven skin tone.
-
Nutrition: Nutrients like vitamin D, vitamin E, and antioxidants support healthy melanin synthesis.
5. Melanin Disorders
- Hyperpigmentation: Excess melanin production causes dark patches on the skin. Common examples include melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Hypopigmentation: Reduced melanin production leads to lighter skin patches, as seen in conditions like vitiligo and albinism.
- Melanoma: A type of skin cancer originating from melanocytes, often linked to excessive UV exposure.
6. Boosting or Reducing Melanin Naturally
For those looking to enhance or lighten their pigmentation, here are some tips:
- Boosting Melanin : Consume foods rich in tyrosine, vitamin C, and antioxidants (e.g., berries, nuts, leafy greens). Limit the use of harsh skin-lightening products that may disrupt melanin synthesis.
- Reducing Melanin : Use sunscreen to prevent excessive tanning and pigmentation. Incorporate natural brightening agents like kojic acid and licorice extract into your skincare routine.
7. The Beauty of Diversity
Melanin is a testament to the incredible diversity of human biology. It’s a natural shield and an aesthetic hallmark that varies across populations, celebrating the uniqueness of every individual. Embracing your melanin—in all its forms—is a step toward appreciating the intricate beauty of nature.

ResearchGate - Melanin biosynthesis in bacteria, regulation and production perspectives licensed under CC BY 2.0
8. Conclusion
Understanding melanin gives us a deeper appreciation of its protective and aesthetic roles. Whether you’re basking in the sun or shielding yourself from it, your melanin works tirelessly to maintain your skin’s health and integrity. Celebrate this miraculous pigment and the unique identity it provides—a true masterpiece of biology.